GAM - Thematic Thoughts: Geopolitics And Green Economy Disruptions In Asia Pacific
More than ever before, Asia Pacific producers are key players in the global clean energy revolution.

With geopolitical tensions rising and the threat of disruption looming ever larger, Gam Investments’ Meera Patel explores factors behind the risks and opportunities for investors in a region harnessing the might of the green economy to bolster its long-term economic prospects.
Over the past decade, we have witnessed the emergence of a growing sustainability community in Asia Pacific spanning governments, corporates and investors. This is primarily due to the region’s significant role from an economic, demographic and emissions perspective, but also a growing necessity as the impacts of climate change are experienced firsthand.
Green economy supply chains are now more reliant on Asian production than ever, with China dominating solar panel, critical mineral processing and battery production, while Japan and South Korea lead on green hydrogen strategy and commercialisation driving regional trade agreements.
Amid rising geopolitical tensions and a continuing wave of election surprises, major Asian economies using the green economy as a driver to boost future growth and enhance energy security are exposed to the uncertainty around global regulatory repeals creating both tailwinds and headwinds.
Why does this matter?
Since the US signed its mighty USD 370 billion Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) into law in August 2022 [1], Asia’s clean energy supply chains and Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) levels have been negatively impacted, with the UN Trade and Development’s 2024 World Investment Report estimating an 8% decrease in FDI in developing Asia during 2023. [2]
Aimed at lowering energy costs for US households and businesses by accelerating private investment in clean energy solutions, strengthening local supply chains and creating local employment opportunities, the IRA has redirected investment flows amid a challenging high interest rate environment and oversupply dilemma for clean energy stocks.
Foreign direct investment (FDI) by region, billions of dollars, per cent, 2022-2023
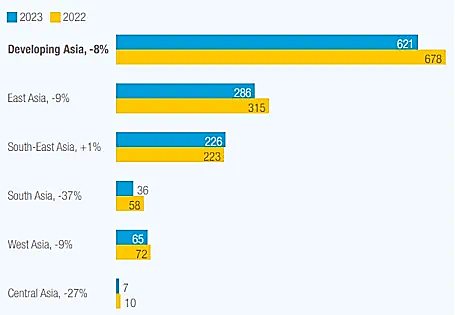
Source: UN Trade and Development (UNTAD)
A Republican sweep in November’s US Presidential elections could potentially weaken the rollout and implementation of the IRA, with consumer-facing incentives such as electric vehicle (EV) tax credits and highly technology-dependent sectors such as hydrogen and carbon capture facing the most pressure. It is also likely that a renewed focus on foreign entity concerns will dominate headlines, negatively impacting Chinese EV and clean energy sectors.
What is the opportunity from an investment perspective?
Republican-controlled states have received the majority of benefits from an IRA-driven manufacturing revival and associated job creation, so it is highly unlikely that all support will be repealed regardless of which party wins in November. Given the challenges behind aging infrastructure, utility-scale solar and energy storage manufacturing will remain key strategic priorities and have dominated new facilities announcements to date. Several Korean clean energy companies in this space are well positioned to benefit from continued support and provide the added integration benefit of operating across all key solar supply chains while investing in leading battery coating technology which could lower costs by 17%-30%. [3]
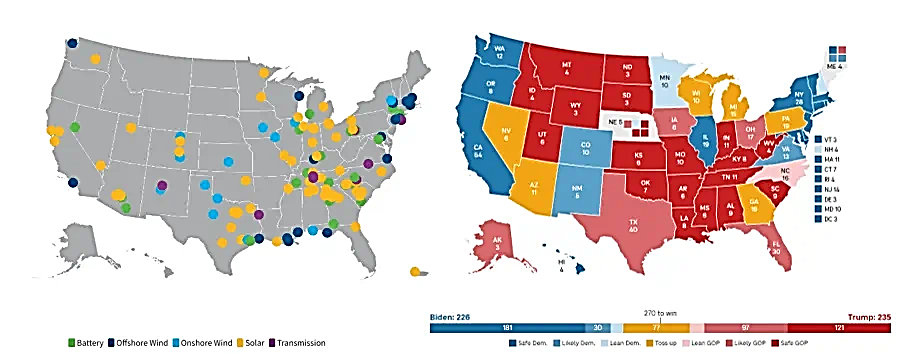
Source: American Clean Power (cleanpower.org)
Source: NPR
Asia accounts for over two thirds of global heavy industry capacity, and it is currently widely accepted that the only way to get these industries to net zero at the required scale is via three advanced technologies: electric arc furnaces, hydrogen and carbon capture. Although a number of decarbonisation project proposals have been announced by leading industrial companies, energy inefficiencies and cost remain primary inhibitors to scaling up these technologies. However, on a relative basis, Asia has made significant progress. For example, this is evident by China’s ability to produce hydrogen at approximately half the cost of European equivalents, enabling scalability of electrolysers and the knock-on impact of rapid cost deflation as seen with other parts of the clean energy value chain. Any IRA-related repeals on hydrogen and carbon capture could provide an added tailwind to Asian companies.
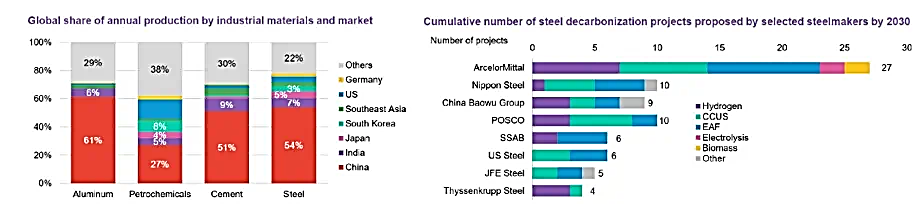
Source: BNEF
There is one legacy energy source most countries and policymakers seem to agree on as being critical to meeting net zero targets: nuclear’s role in the energy mix. Although the transition from coal and gas-fired facilities to atomic plants is well underway, engineering challenges remain an issue. In the short term, the US ban on imported uranium products from Russia, which accounts for 40% of global capacity4, could tighten supplies with two leading European-based uranium enrichment companies set to benefit from this disruption. In Asia, as part of the Sapporo 5 partnership, Japan has committed to increase their enrichment from 75 tons to 450 tons per year by 20275, while China has spent the last two decades becoming increasingly self-sufficient in this area.
Although geopolitical dynamics remain unpredictable, understanding the impact of various scenarios is key to identifying risks, inflationary pressures and both the progress or derailing of ambitious net zero goals.
[1] International Energy Agency, November 2023
[2] UNCTAD
[3] Bloomberg
[4] Bellona
[5] US Department of Energy
Important legal information
The information in this document is given for information purposes only and does not qualify as investment advice. Opinions and assessments contained in this document may change and reflect the point of view of GAM in the current economic environment. No liability shall be accepted for the accuracy and completeness of the information. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results or current or future trends. The mentioned financial instruments are provided for illustrative purposes only and shall not be considered as a direct offering, investment recommendation or investment advice. The securities listed were selected from the universe of securities covered by the portfolio managers to assist the reader in better understanding the themes presented and are not necessarily held by any portfolio or represent any recommendations by the portfolio managers. There is no guarantee that forecasts will be realised.
